Last edit: 11/05/2023
The safety goals of this European Standard shall include:
- choice of materials such that the construction and operation of the system are not detrimentally affected. In particular, all the components of the fuel pipework shall be capable of withstanding the mechanical, chemical and thermal loads to which they can be subjected during normal operation;
- reliable and correct time for ignition of the fuel/air-mixture at the burner(s);
- prevention of unintentional release of unburned fuels;
- shut-off fuel-supply in case of relevant fault;
- protection of pipeline by precluding the propagation of flame in reverse flow;
- prevent firing when the exhaust of combustion products is not ensured;
- prevent firing when the process conditions are not in the safe state
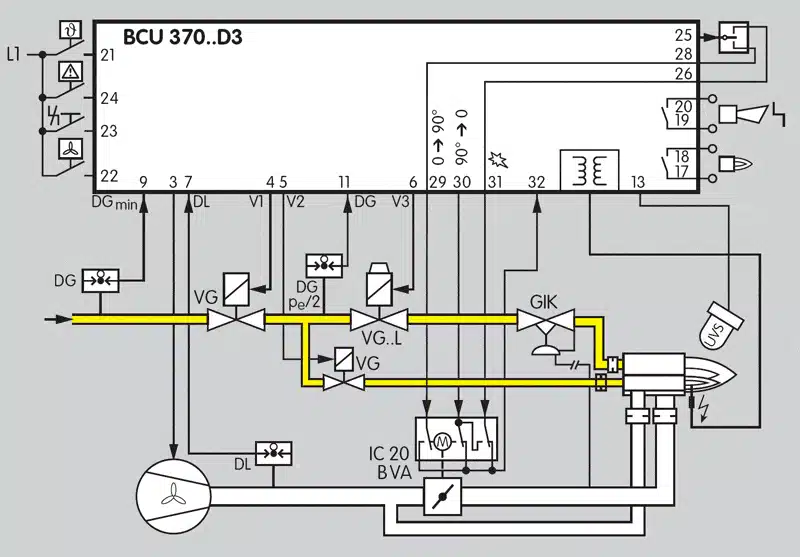
Required safety devices
The safety devices of a combustion system to which EN 746-2 refers are the following:
- Manual isolating valve;
- Filter/strainer;
- Automatic shut-off valves;
- Gas pressure regulator;
- Air and gas flow and pressure detectors;
- Flue gas venting;
- Ignition system;
- Individual manual shut-off valves for burners.

Combustion Air and Air / Gas fuel ratio
The pipework to be designed shall take into account the properties of the combustion air.
All manual control devices (registrers, valves, etc.) for the air shall be set in their pre-determined positions and protected against inadvertent movement.
The ventilation of IThE shall be such as to allow an adequate supply of process air and combustion air to reach the burner under all conditions.
The standard EN 746-2 requires that a burner is always ignited with a stable air-gas mixture. The air / gas ratio controllers allows to satisfy this request.
Combustion ratio control (GARC) is a safety requirement; if this ratio exceeds the required tolerances, it can cause the flame to go out or create a dangerous situation, resulting from the formation of an explosive mixture inside the combustion chamber.
Burners and Control systems
All burners shall be suitable for working conditions and shall provide operating safety for:
- The fuels used (type, pressure, etc …);
- Operating conditions (pressure, temperature, atmosphere, etc …);
- The nominal input rate and range of regulation (maximum and minimum capacity);
- Ease of visual monitoring (sight glasses,sight holes, etc.).
The main and pilot flame shall also be adequately controlled.
Flame control typically takes place with electronic devices which, connected to flame detectors, control the correct ignition of the flame and the correct steady state operation.